Recognizing the early signs of autism in toddlers is crucial for early intervention and support. By identifying these signs between the ages of 18 to 24 months, parents and caregivers can take the necessary steps to ensure their child receives the appropriate evaluations and interventions. This proactive approach can significantly improve outcomes and enhance the child’s developmental trajectory .Moreover, engaging in home ABA therapy can provide tailored support and interventions in familiar environments, fostering optimal learning and skill development.

Importance of Early Screening
Early screening for autism is highly recommended as it allows for timely intervention and therapy. Research has shown that the younger a child starts therapy, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), the better the outcomes. Early screening can help identify any developmental delays or atypical behaviors that may indicate the presence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Signs Between 18-24 Months
Between 18 to 24 months of age, it is important to look out for certain signs and behaviors that may suggest the presence of autism. While these signs may vary from child to child, here are some common indicators to be aware of:
Communication Delays
One of the key signs of autism in toddlers is a delay in communication skills. This can manifest as a lack of babbling or limited gestures such as pointing or waving. The child may also struggle with making eye contact or responding to their name when called.
Behavioral Patterns
Autistic toddlers may exhibit repetitive behaviors or engage in restricted interests. They may develop specific routines or rituals and become upset or distressed if these routines are disrupted. Furthermore, they may exhibit repetitive body movements such as hand flapping or rocking.
Sensory Sensitivities
Many children with autism have sensory sensitivities, meaning they may be overly sensitive or underresponsive to sensory stimuli. They may become overwhelmed by certain sounds, textures, or lights. Additionally, they may show a preference for repetitive activities that involve sensory input, such as spinning or flicking objects.
It is important to note that while these signs may indicate the possibility of autism, a formal diagnosis should be sought from medical specialists such as developmental pediatricians, child psychiatrists, or pediatric neurologists. These professionals have the expertise to conduct a comprehensive evaluation and provide an accurate diagnosis.
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in observing and reporting any concerns about their child’s development. They are often the first to notice signs of developmental delays and can correctly identify a significant percentage of children with disabilities. By being vigilant and seeking appropriate evaluations, parents can ensure that their child receives the necessary support and interventions for their unique needs.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
When it comes to the diagnosis of autism, a comprehensive evaluation is crucial to ensure accurate identification and appropriate intervention. Medical specialists play a crucial role in this process, along with the utilization of screening tools specifically designed for autism.
Medical Specialists’ Role
Medical specialists, such as developmental pediatricians, child psychiatrists, and pediatric neurologists, have the expertise to evaluate and diagnose autism spectrum disorder (ASD). These professionals assess the child’s development, behavior, and communication skills to determine if they meet the criteria for an autism diagnosis.
During the evaluation, the medical specialist will typically conduct a thorough medical history review, observe the child’s behavior, and may request additional assessments or tests to rule out other possible causes for the observed symptoms. They work closely with other professionals, such as speech therapists and psychologists, to gather a comprehensive understanding of the child’s condition.
Screening Tools for Autism
Screening for autism is recommended for children between the ages of 18 to 24 months, as early detection and diagnosis can lead to the initiation of therapies. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends autism screenings at 18 and 24 months during well-child visits, with additional screenings for infants with risk factors.
Parents are often the first to notice signs of developmental delays in their children.. Screening tools are used to assess autism in children and aid in the diagnostic process. Two commonly used screening tools for children under 30 months are the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) and the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers, Revised with Follow-Up (M-CHAT-R/F).
These screening tools consist of a series of questions that assess the child’s behaviors and communication skills. They help identify potential red flags for autism and guide medical professionals in determining the need for further evaluation and diagnosis.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for children with autism, as research has shown that they lead to better long-term outcomes. A study published in JAMA Pediatrics found that infants with early signs of autism who received preemptive therapy intervention experienced a reduction in autism severity across early childhood and had lower odds of being diagnosed with ASD at 3 years of age.
By involving medical specialists and utilizing screening tools, parents and caregivers can ensure that their child receives the appropriate evaluation and diagnosis. Early detection paves the way for timely intervention and access to therapies that can significantly impact a child’s development and improve their long-term outcomes.
Signs of Autism at Age Two
Identifying signs of autism in children at the age of two is crucial for early intervention and support. While every child develops at their own pace, there are certain behavioral and developmental patterns that may indicate the presence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In this section, we will explore three key signs to look out for at age two: communication delays, behavioral patterns, and sensory sensitivities.
Communication Delays
One of the most common signs of autism in a two-year-old is a delay in spoken language development. Children with autism may exhibit difficulties in communication, such as limited vocabulary, difficulty expressing their needs and emotions, or a lack of interest in engaging in conversations. They may also have challenges with nonverbal communication, such as maintaining eye contact, understanding gestures, or using appropriate facial expressions.
It’s important to note that not all children with autism will have the same communication delays. Some children may have relatively strong verbal skills but struggle with social communication, while others may have significant difficulties in both areas.
Behavioral Patterns
Another sign of autism in a two-year-old is the presence of repetitive and stereotypical behaviors. These behaviors can manifest in various ways, such as repeating certain actions (e.g., lining up toys, spinning objects), having specific routines or rituals, or showing intense interests in specific topics. Children with autism may also display resistance to change and difficulty adapting to new situations.
Additionally, some children with autism may exhibit challenging behaviors, such as meltdowns or tantrums, in response to sensory overload or difficulties in expressing their needs. These behaviors can vary in severity and frequency, depending on the individual.
Sensory Sensitivities
Sensory sensitivities are common among individuals with autism, and these sensitivities can become apparent at a young age. Children with autism may display aversions or sensitivities to certain sounds, textures, tastes, or smells. They may react strongly to stimuli that others may not find bothersome, such as covering their ears when exposed to loud noises or becoming distressed by certain clothing fabrics.
It’s important to remember that not all children with autism will experience the same sensory sensitivities, and the specific sensitivities can vary widely among individuals.
By recognizing these signs of autism at age two, parents and caregivers can take proactive steps to seek further evaluation and support from medical professionals. Early detection and intervention play a critical role in promoting the child’s development and enhancing their overall quality of life.
Diagnostic Process
When it comes to diagnosing autism in toddlers, a comprehensive evaluation is necessary to accurately identify the signs and symptoms. The diagnostic process typically involves a psychological evaluation and may also involve the expertise of speech therapists, also known as speech-language pathologists.
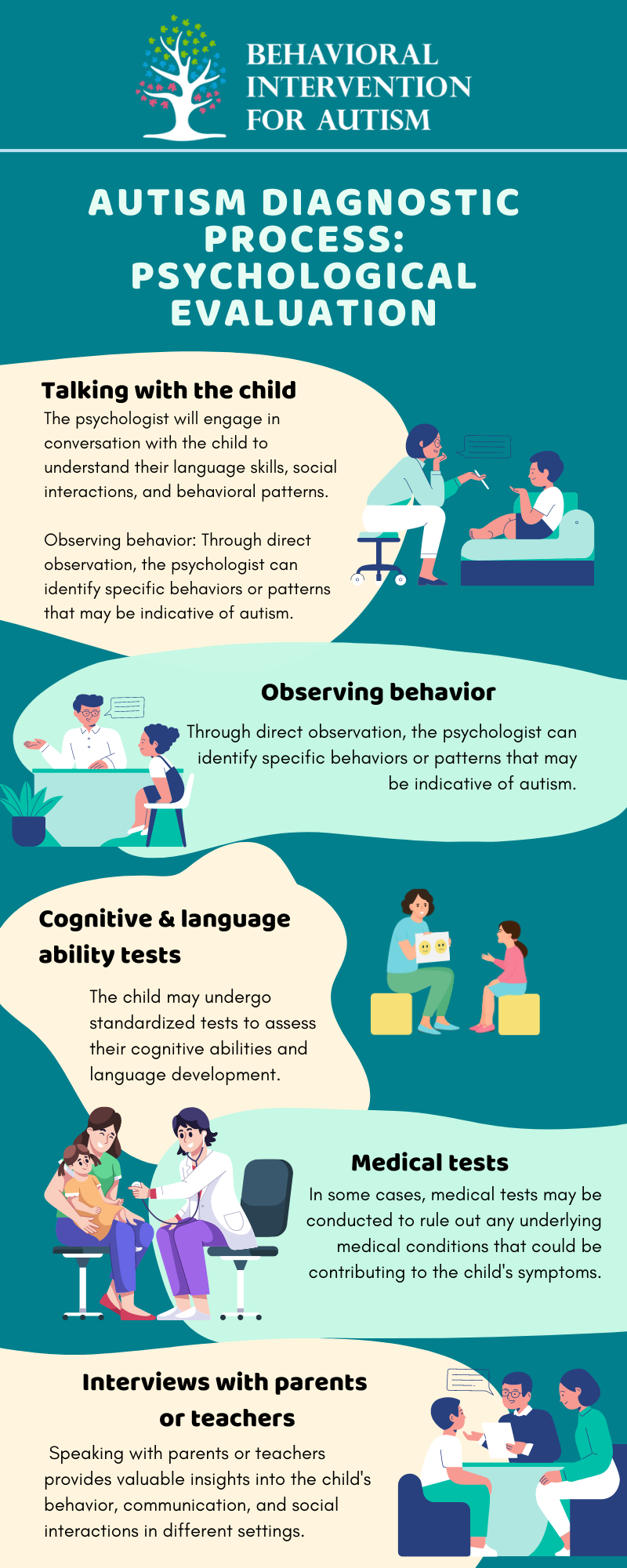
Psychological Evaluation
A crucial component of the diagnostic process for autism is a psychological evaluation. Psychologists who specialize in autism utilize various methods to gather information and assess the child’s development. These methods may include:
By utilizing these evaluation methods, psychologists can gather comprehensive information about the child’s developmental profile, which aids in making an accurate diagnosis of autism.
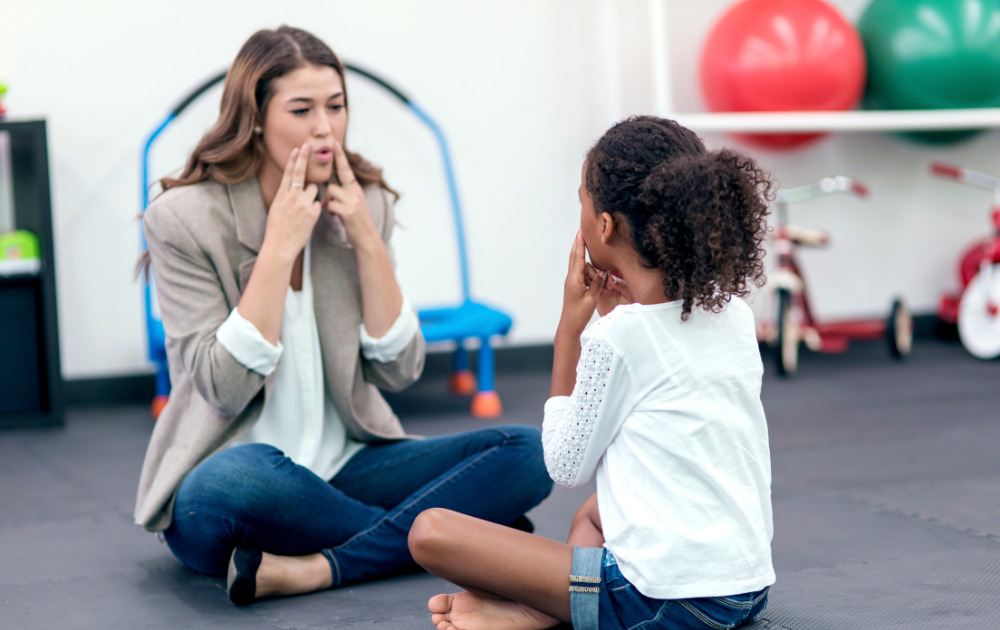
Role of Speech Therapists
Speech therapists, or speech-language pathologists, play a crucial role in the diagnostic process and ongoing treatment of individuals with autism. When it comes to diagnosing autism, speech therapists assess the child’s communication skills, strengths, and challenges. They use their expertise to identify any language delays or difficulties in social communication.
In addition to their diagnostic role, speech therapists develop tailored treatment plans to address the specific needs of each child. These plans often incorporate various therapeutic techniques, such as play-based activities, storytime, or movement-based activities, to engage with the child and improve their communication skills.
Speech therapists work closely with the child and their family to provide ongoing support and intervention. They help the child develop verbal and non-verbal communication skills, enhance social interactions, and improve overall communication abilities. The involvement of speech therapists is essential in promoting language development and facilitating effective communication for individuals with autism.
By combining the expertise of psychologists and speech therapists, a comprehensive diagnostic process can be carried out, leading to early identification and intervention for children with autism. This early intervention is crucial for providing the necessary support and resources to help individuals with autism thrive and reach their full potential.
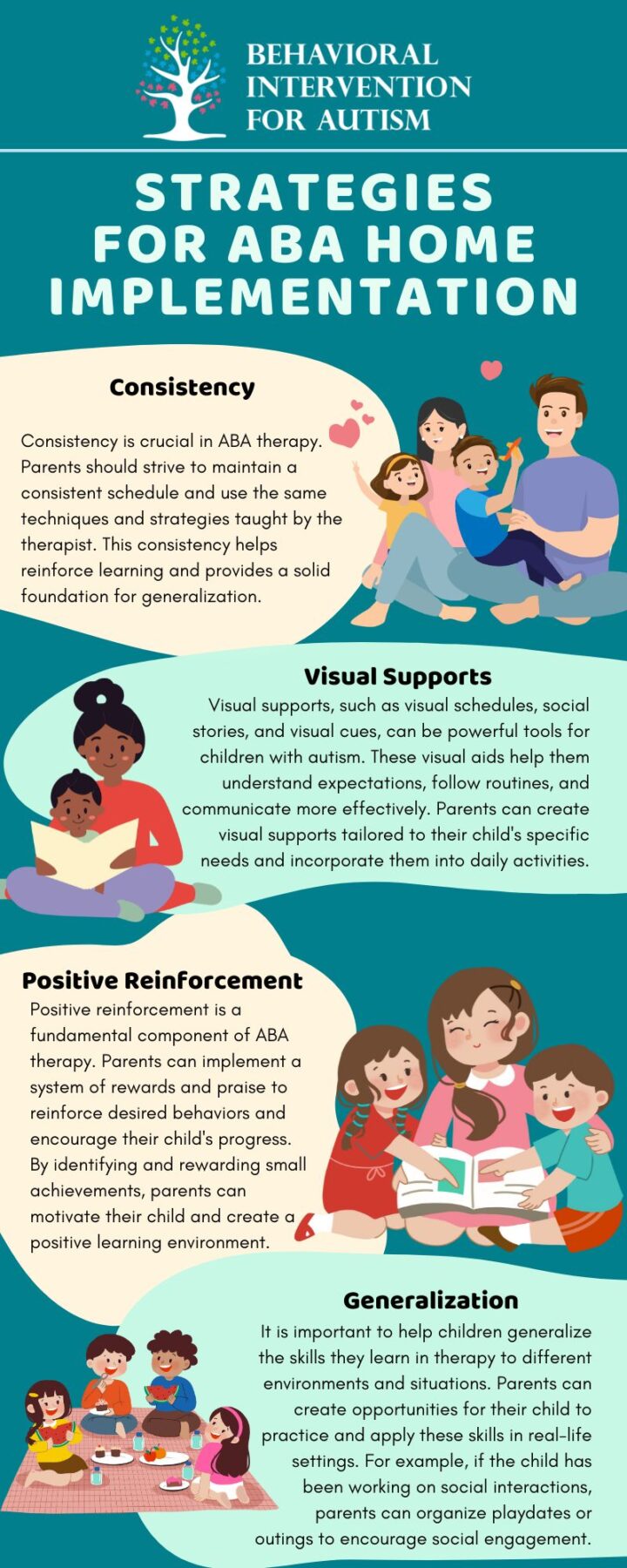
Therapy and Intervention
Therapy and intervention play a vital role in promoting their development and overall well-being. Two important aspects of therapy and intervention include tailored treatment plans and the use of assistive devices for communication.
Tailored Treatment Plans
Every individual with autism is unique, and as such, their therapy and intervention should be tailored to their specific needs. Tailored treatment plans are designed to address the individual’s strengths, challenges, and goals. These plans are typically created by a team of professionals, including medical specialists, psychologists, speech therapists, and educators.
A tailored treatment plan may include a combination of various therapies, such as behavioral therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training. The specific components of the plan will depend on the individual’s needs and areas of focus. Regular evaluation and reassessment are crucial to ensure that the treatment plan remains effective and can be adjusted as needed.
By tailoring the treatment plan to the unique needs of the individual, therapy and intervention can address specific challenges associated with autism and help individuals reach their full potential.
Assistive Devices for Communication
Communication can be a significant challenge for individuals with autism, particularly for those who are nonverbal or have limited verbal abilities. Assistive devices and technologies can play a crucial role in facilitating effective communication.
Speech therapists, also known as speech-language pathologists, can provide invaluable assistance in this area. They assess the individual’s strengths and challenges and develop strategies to enhance their communication skills. Speech therapists may use a variety of methods, including play, storytime, or movement activities, to engage with the individual and facilitate their communication.
Assistive devices and technologies are also utilized to support communication efforts. These devices can include sign language, Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS), communication applications on tablets, or speech output devices. These tools empower nonverbal individuals with autism to express their needs, thoughts, and emotions effectively.
By incorporating assistive devices for communication into therapy and intervention, individuals with autism can overcome communication barriers and enhance their overall quality of life.
Therapy and intervention provide a foundation for individuals with autism to develop important skills, improve communication abilities, and navigate the world around them. Through tailored treatment plans and the use of assistive devices, individuals with autism can access the support and resources they need to thrive and reach their full potential.
Sources:
https://www.expressable.com/learning-center/autism/what-are-the-signs-of-autism-in-a-2-year-old