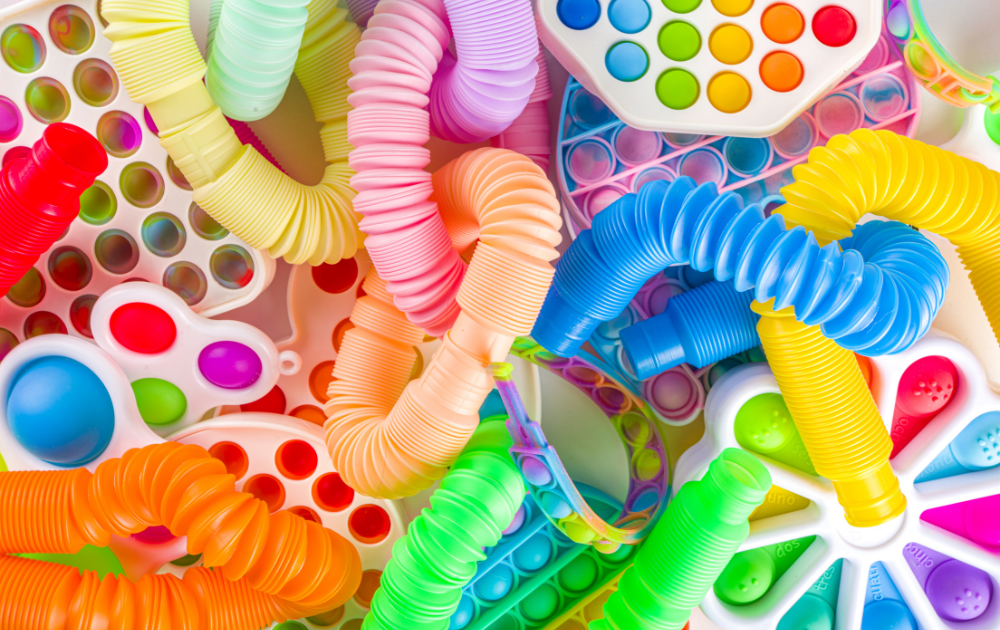
Fidget toys offer significant benefits for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). They serve as valuable tools for managing symptoms, providing therapeutic advantages for both children and teens on the spectrum.
Benefits for Autism
Fidget toys serve as effective sensory-based interventions that can greatly enhance the functionality of individuals with autism. By incorporating fidget toys into therapy and daily routines, children and teens with autism can experience improved emotional regulation and a reduction in unwanted behaviors. The tactile stimulation provided by fidget toys such as the Marble Maze Mat, Magnetic Fidget Spinner Rings, and Textured Stretchy Strings can offer a safe and beneficial outlet for individuals with autism, aiding in stress relief and focus.
Suitable Age Range
Selecting fidget toys for individuals with autism requires careful consideration of age, as it influences the choice of appropriate options. While these toys can benefit various age groups, it’s crucial to ensure they are safe, engaging, and developmentally suitable for each individual’s needs.
It is important to note that the suitability of a fidget toy may vary based on the unique sensory preferences and sensitivities of the individual with autism. Therefore, parents, caregivers, and therapists should carefully evaluate the age appropriateness and sensory features of each fidget toy to ensure optimal benefits for the individual.

Types of Fidget Toys
Selecting suitable fidget toys for individuals with autism involves considering various options that cater to different sensory needs and preferences.
These toys offer a range of shapes, textures, and forms, providing diverse stimuli for tactile exploration and engagement.
Variety of Options
The best fidget toys for autism offer a diverse array of options to keep hands busy and minds focused. These toys can encourage exploration and manipulation through activities like squeezing, squishing, throwing, and catching. They come in different sizes, shapes, textures, and colors, including light-up, squishy, and tactile varieties.
One of the key aspects of fidget toys is their versatility in meeting the unique sensory requirements of individuals with autism. By offering a wide selection of options, caregivers and parents can find the most suitable toy that resonates with the specific needs and preferences of their child.
Texture and Shapes
Texture and shape play a significant role in the effectiveness of fidget toys for individuals with autism. The tactile feedback provided by textured surfaces can offer calming and soothing sensory input, aiding in emotional regulation and attention redirection.
Shapes also contribute to the sensory experience of fidget toys. From traditional stress balls to intricate puzzles, the variety of shapes available allows individuals to engage in different types of manipulation and fine motor activities. Additionally, the visual appeal of unique shapes can enhance the overall sensory experience and engagement with the toy.
Recommended Fidget Toys
Choosing the right fidget toys for individuals with autism significantly impacts their well-being and development. Selecting toys that provide safe and beneficial stimulation is crucial for emotional regulation and minimizing undesirable behaviors.
Here are three recommended fidget toys that have proven valuable for children and teens with autism:
Marble Maze Mat
The Marble Maze Mat is a tactile and engaging fidget toy that captures the attention of individuals with autism, providing a calming yet stimulating activity. By maneuvering the marbles through the maze, users can enhance their fine motor skills while also promoting focus and concentration. The visual and tactile feedback offered by the Marble Maze Mat can aid in reducing anxiety and improving sensory processing.
Magnetic Fidget Spinner Rings
Magnetic Fidget Spinner Rings are a versatile fidget toy that can be used discreetly and conveniently to address sensory needs. These rings are designed to spin effortlessly, offering a satisfying sensory experience that helps individuals with autism channel their energy and improve concentration. The quiet, non-disruptive nature of Magnetic Fidget Spinner Rings makes them suitable for use in various environments, including classrooms and public settings.
Textured Stretchy Strings
Textured Stretchy Strings are a tactile and flexible fidget toy that promotes sensory exploration and tactile stimulation. Individuals with autism can stretch, twist, and manipulate these strings to soothe anxieties and improve focus. The varying textures on the strings provide a sensory-rich experience that can be comforting for individuals who seek tactile input. Textured Stretchy Strings are portable and easy to carry, making them a convenient sensory tool for on-the-go use.

More Recommended Fidget Toys
Certain fidget toys can provide unique sensory experiences that help individuals with autism relax, focus, and develop fine motor skills.
Here, we explore three highly recommended options: the Orbit Ball Fidget Toy, Shape-Changing Robot Toy, and Transformable Fidget Spinner.
Orbit Ball Fidget Toy
The Orbit Ball Fidget Toy is designed to provide tactile and visual stimulation, offering a soothing and engaging experience for individuals with autism. This toy allows for fluid movements and encourages hand-eye coordination, fine motor skills, and sensory exploration. The Orbit Ball Fidget Toy is not only entertaining but also serves as a tool for stress relief and relaxation.
Shape-Changing Robot Toy
The Shape-Changing Robot Toy is a versatile fidget toy that offers both tactile and visual sensory input. This toy engages individuals with autism in imaginative play, as they can transform the robot into various shapes and forms. The act of manipulating the toy promotes dexterity, creativity, and cognitive skills. The Shape-Changing Robot Toy provides a dynamic sensory experience that can help individuals with autism focus and unwind.
Transformable Fidget Spinner
The Transformable Fidget Spinner is a multifunctional fidget toy that combines the benefits of traditional spinners with creative construction elements. This toy offers a hands-on sensory experience through spinning, twisting, and transforming its shape. The Transformable Fidget Spinner not only aids in promoting focus and stress relief but also enhances cognitive abilities and problem-solving skills. It is a portable and durable option for individuals with autism to engage with their senses and emotions actively.

Additional Sensory Tools
Supporting individuals with autism and addressing sensory challenges involves utilizing various sensory tools that enhance focus, self-regulation, and emotional well-being.
Additional sensory tools that have proven beneficial for individuals on the autism spectrum are highlighted.
Simple Dimple Fidget Toy
The Simple Dimple Fidget Toy is a favored choice for individuals with autism due to its effectiveness in redirecting attention and promoting calmness in various situations. This compact and quiet fidget toy is well-received by children and has shown to be particularly helpful in providing sensory stimulation. The Fat Brain Simple Dimple is often recommended for its durable quality and effectiveness compared to generic versions.
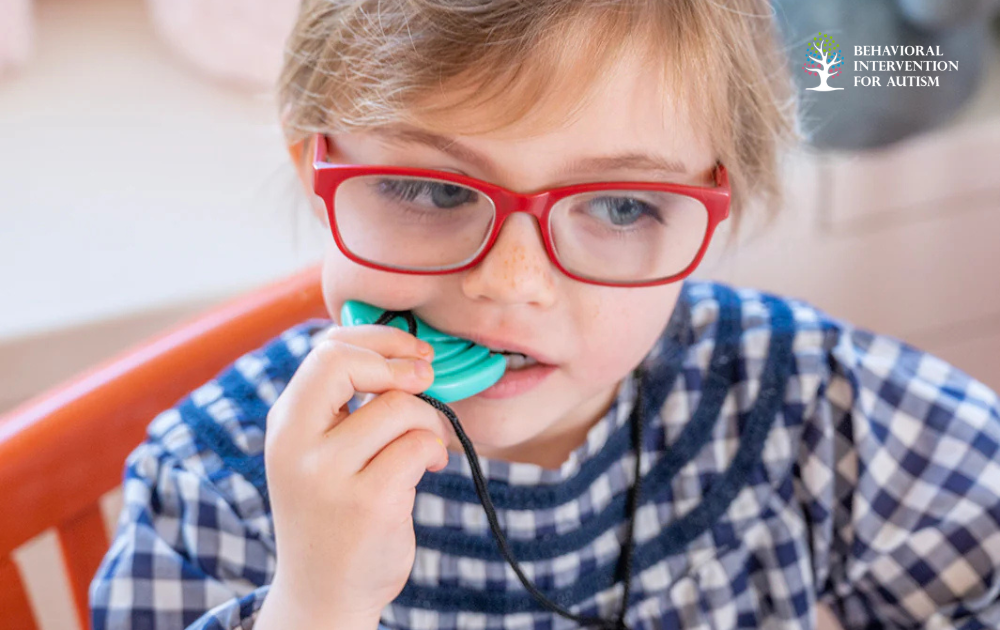
Chew Necklaces
Chew necklaces are popular sensory tools among individuals with autism, especially those who engage in chewing behaviors. These necklaces, designed to withstand vigorous chewing, come in various shapes and designs, such as long Lego blocks or pendant styles. By providing a safe and appropriate outlet for chewing, these necklaces offer sensory input that can help individuals focus and self-regulate.
Waterbead Toys
Waterbead toys, like the Lesong set, have gained popularity as engaging sensory tools in educational settings for individuals with autism. These small and durable toys come in a variety of colors and shapes, providing tactile and visual stimulation. Waterbead toys are not only appealing to children but also offer opportunities for sensory exploration and relaxation.
Noise-Blocking Headphones
For individuals with autism who experience hypersensitivity to noise, noise-blocking headphones can be invaluable in managing sensory overload. Brands like Snug offer noise-blocking headphones specifically designed for children, with a range of color options available. By minimizing external noise distractions, these headphones help individuals tolerate noisy environments better, ultimately reducing the impact of noise sensitivity on their well-being.
Fidget toys can be incredibly beneficial for individuals with autism, providing a means to channel nervous energy and enhance focus. From stress balls to sensory rings, these toys offer various tactile experiences that can help promote calmness and concentration. We understand that every individual is unique, and finding the right fidget toy can make a significant difference in their daily life.
Behavioral Intervention For Autism offers a range of ABA programs in Florida tailored to meet each person’s needs, ensuring effective strategies are in place to support their development. Our dedicated team is passionate about creating engaging and personalized experiences. If you’re interested in learning how we can assist you or your loved one, reach out to us today!