Table of Contents
Autism Spectrum Disorder is characterized by a wide range of challenges that individuals may face in areas such as social interaction, communication, and behavior.
It’s worth noting that no two individuals with ASD are the same, as the condition manifests differently in each person. It’s important to recognize that autism is a lifelong condition and there is currently no known cure that can completely “get rid of” autism. However, with appropriate interventions and support, such as In-home ABA Therapy, children with autism can lead fulfilling and meaningful lives.
ASD is a spectrum disorder, meaning that it encompasses a broad range of symptoms and levels of impairment. Some individuals with autism may have significant difficulties in multiple areas, while others may exhibit milder symptoms and be highly functioning.
But is it actually possible to get rid of it? If so, how? Let’s find out!
Early Signs and Diagnosis
The signs of autism spectrum disorder often become noticeable in early childhood, typically between 12 to 24 months of age. However, diagnosis may not occur until later, especially if the symptoms are subtle.
Therefore, parents and caregivers should be aware of potential early signs of ASD, such as:
- Delayed or limited speech development
- Lack of eye contact or social engagement
- Repetitive behaviors or restricted interests
- Difficulty with changes in routine
- Sensory sensitivities or aversions
If you have concerns about your child’s development, it is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your child’s developmental milestones and refer you to a specialist for further assessment if necessary.
Early intervention is crucial, as research has shown that starting supportive therapy as soon as possible is associated with the best outcomes.
Therapeutic Approaches for ASD
Various therapeutic approaches can address the unique needs of individuals with autism. These approaches aim to enhance communication skills, improve behavior, and develop essential life skills.
Let’s look at each of them:
ABA Therapy Overview
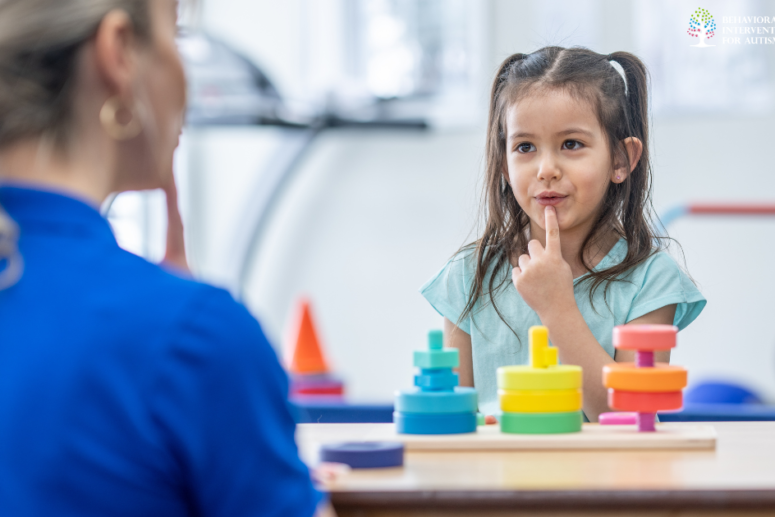
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is considered the most studied and evidence-based intervention for autism. This therapeutic approach focuses on understanding and modifying behavior through methods of repetition and reinforcement.
ABA therapy aims to help individuals with ASD develop social skills, communication abilities, and self-care skills. It also helps reduce problem behaviors.
ABA therapy involves breaking down desired behaviors into small, manageable steps and using positive reinforcement techniques to encourage the development and repetition of those behaviors. Through structured and individualized sessions, ABA therapy can help individuals with autism improve their overall quality of life.
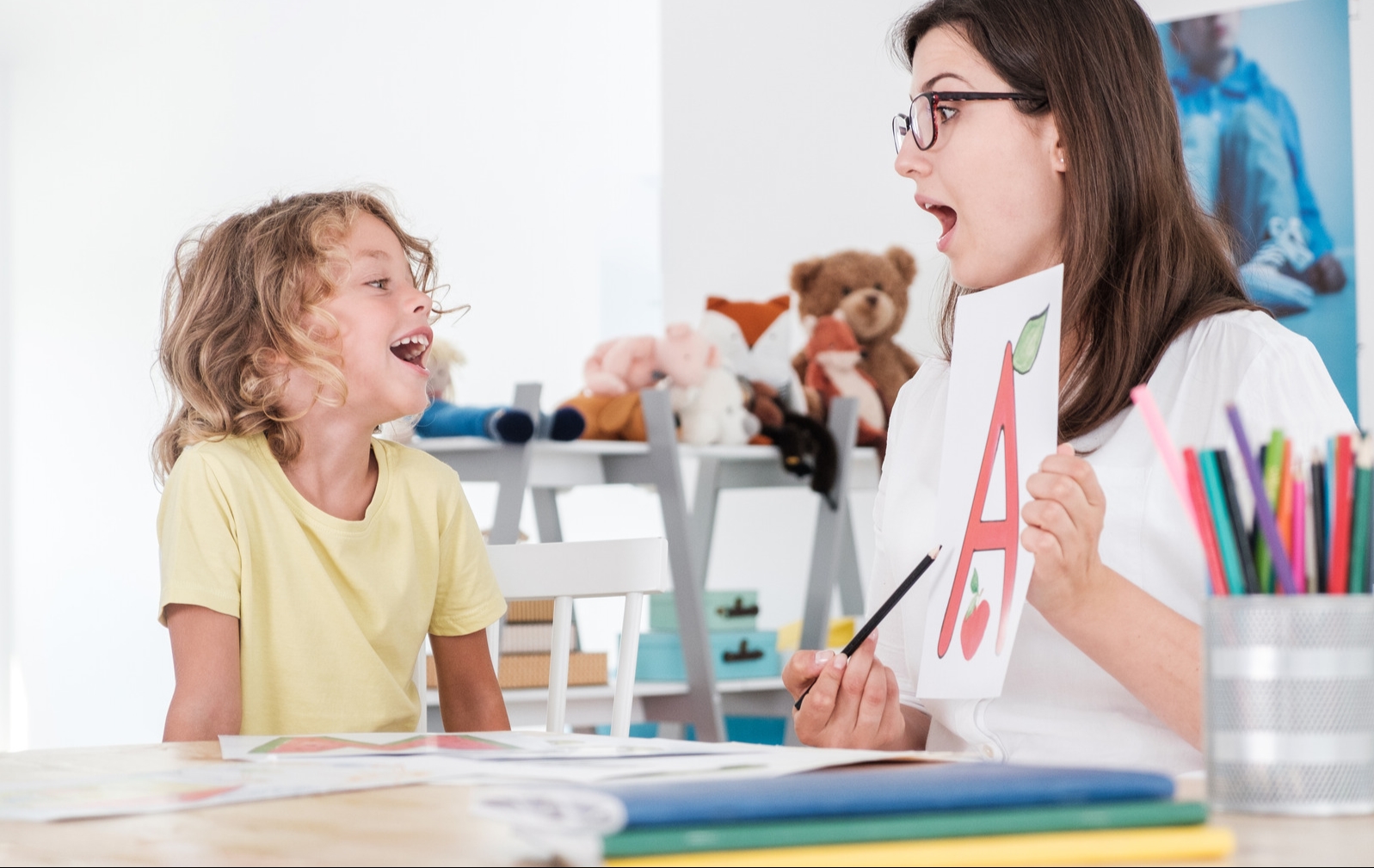
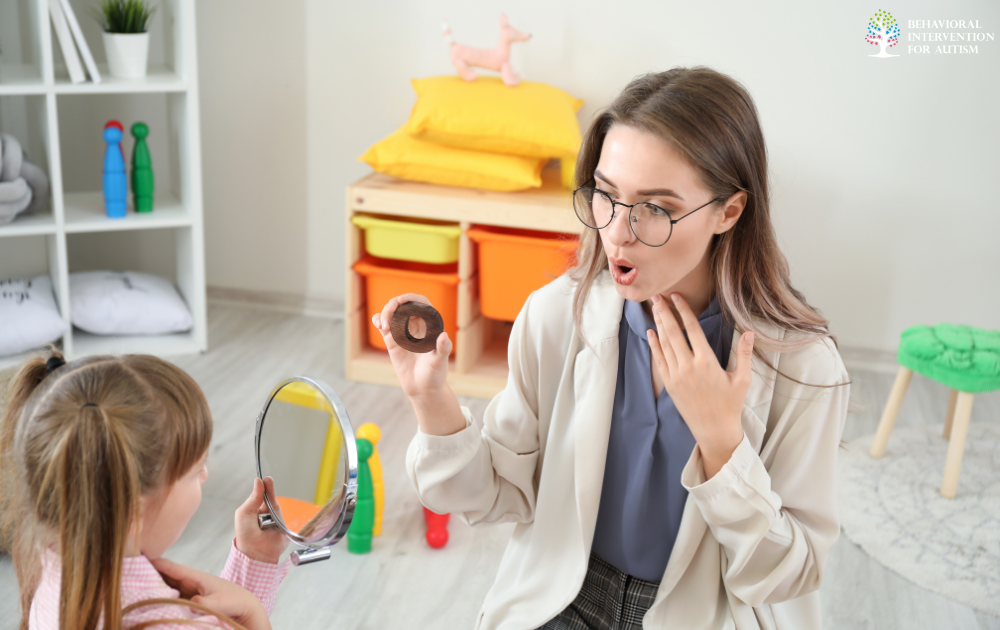
Speech and Communication Therapy
Speech and communication therapy is another crucial therapeutic approach for individuals with ASD. This type of therapy focuses on enhancing both verbal and nonverbal communication skills. Speech therapists work with individuals with autism to improve their speech clarity, language comprehension, and expressive language abilities.
For nonverbal individuals with autism, speech therapists may introduce alternative communication methods, such as signs, gestures, pictures, or electronic speaking devices.
These alternative communication methods enable individuals with limited verbal abilities to express their needs, wants, and thoughts effectively.
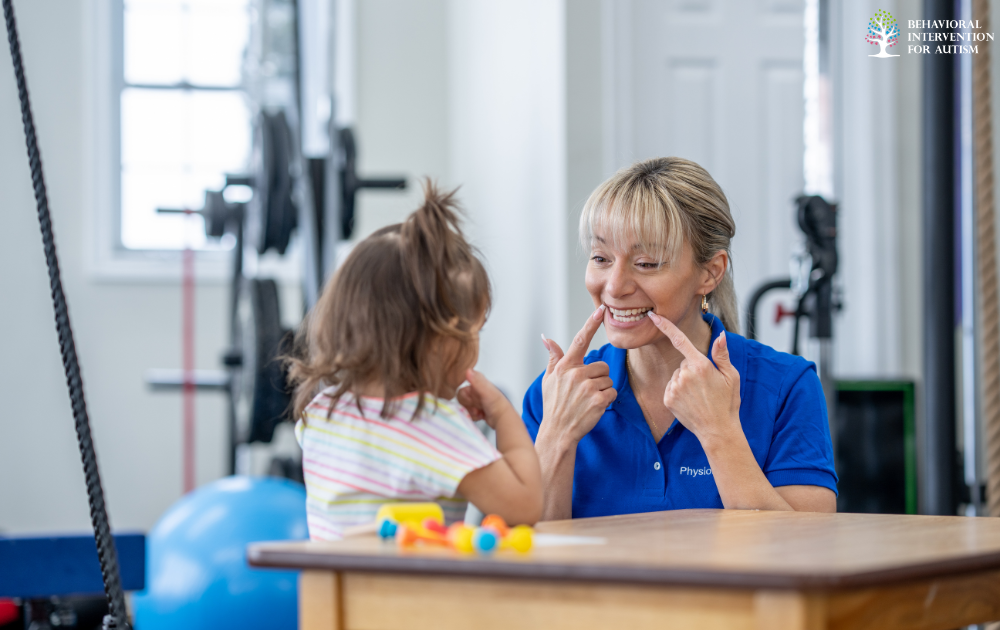
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy plays a vital role in improving the daily life skills and independent functioning of individuals with ASD. Occupational therapists work with individuals to develop the necessary motor, sensory, and self-care skills required for daily activities.
This therapy helps individuals with autism improve their fine motor skills, sensory integration, and self-regulation abilities. Occupational therapists also assist in developing routines and strategies to address sensory sensitivities and challenges that individuals with autism may face.
By incorporating activities tailored to the unique needs of individuals with ASD, occupational therapy aims to enhance their overall independence and quality of life.
Treatment Strategies for ASD
A comprehensive and individualized approach is key to addressing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Treatment strategies for children with ASD typically involve a combination of therapies, educational interventions, and, in some cases, medication.
In this section, we will explore three important treatment strategies which are as follows:
Individualized Education Plans (IEP)
An Individualized Education Plan (IEP) is a crucial component of educational support for children with ASD. Developed collaboratively with parents, educators, and a team of professionals, an IEP outlines specific goals, accommodations, and support services tailored to the child’s unique needs.
IEPs focus on improving communication, behavior, socialization, and self-care skills. They provide a roadmap for teachers and therapists to implement evidence-based interventions and monitor the child’s progress.
Addressing the individual needs of children with ASD allows IEPs to significantly enhance their educational experience and help them reach their full potential.
Medication Considerations
In some cases, medication may be considered as part of the treatment plan for children with ASD.
Medications such as Risperidone (Risperdal) and Aripiprazole (Abilify) have been FDA-approved to help manage irritability and aggression in children with ASD. These medications are typically used in conjunction with behavioral therapies and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It’s important to note that medication is not a cure for ASD, but it can help alleviate specific symptoms that may significantly impact a child’s daily functioning. The decision to use medication should be carefully considered.
Also, regular monitoring and close communication with a healthcare provider are essential when medication is part of the treatment plan.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to traditional therapies, some parents and caregivers explore alternative therapies to complement the treatment of ASD. It’s important to approach alternative therapies with caution and consult with healthcare professionals to ensure safety and efficacy.
While there is no research supporting the removal of gluten or casein from the diet as a helpful treatment for ASD, proper nutrition is important for overall health and well-being.
Alternative therapies can vary widely and may include interventions such as music therapy, art therapy, animal-assisted therapy, and sensory integration therapy. These therapies aim to address specific challenges associated with ASD, such as sensory sensitivities, social interactions, and emotional regulation.
When considering alternative therapies, it’s important to gather information, seek recommendations from professionals, and make informed decisions tailored to the child’s unique needs.
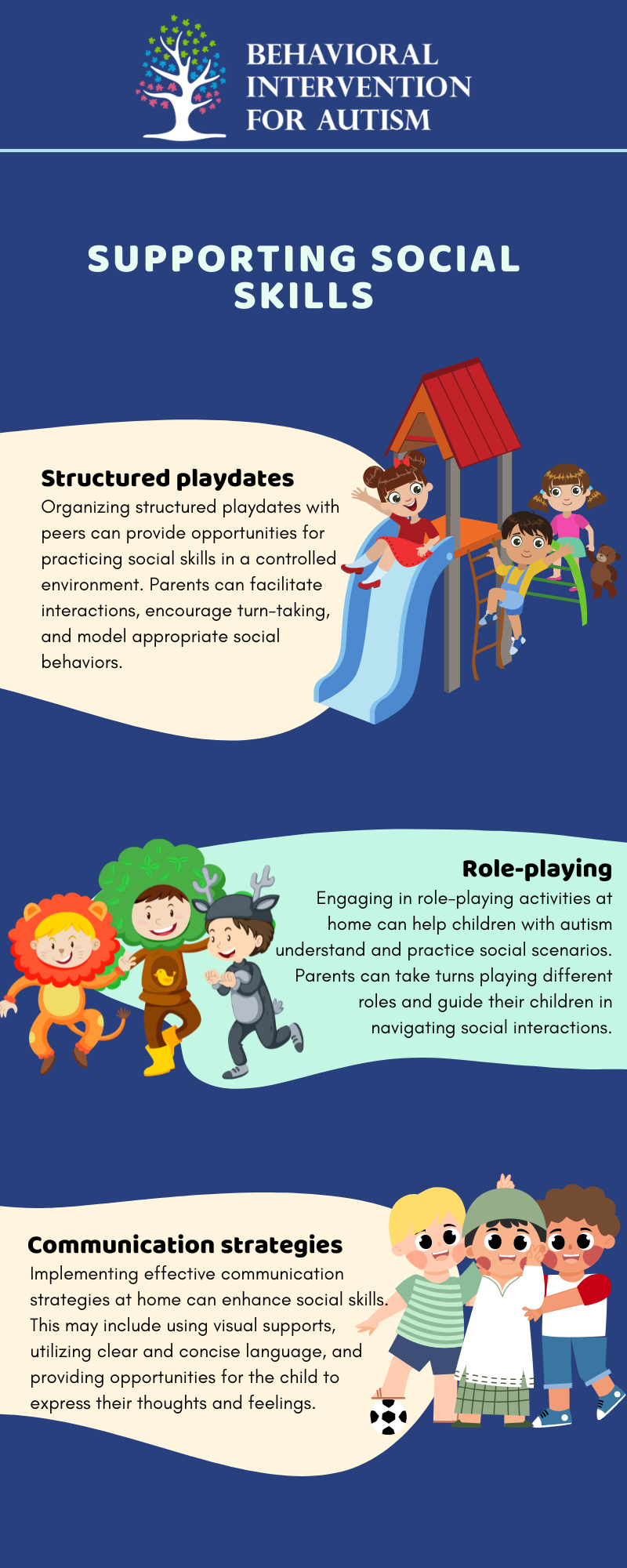
Supporting Social Skills
Developing social skills is an essential aspect of a child’s development, particularly for individuals with autism. Parents can play an active role in supporting and enhancing their child’s social skills.
In the illustration below, we’re going to take a look at some of the most effective strategies parents can implement:
Always keep in mind that every child with autism is unique, and it’s essential to tailor interventions to their specific needs and strengths. If you need additional support and guidance, it’s highly recommended to consult with professionals and join support networks for more valuable resources and insights.
Sources:
https://www.webmd.com/brain/autism/understanding-autism-treatment
https://www.healthline.com/health/can-autism-be-cured
https://www.verywellhealth.com/low-cost-autism-therapies-parents-can-provide-at-home-4172365
https://www.tpathways.org/faqs/can-autism-be-cured
- 9 Common Obsessions of Children With Autism You Should Know - February 25, 2025
- What is Neurodiversity? A Guide to Embracing Differences - February 25, 2025
- Understanding Hyperfocus in Autism: What It Means and Why It Happens - February 25, 2025