
Table of Contents
Short-term memory, often referred to as working memory, plays a crucial role in everyday functioning, enabling individuals to hold and manipulate information temporarily. In the context of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), understanding the nuances of short-term memory can shed light on various cognitive strengths and challenges faced by individuals on the spectrum. This article delves into the role of short-term memory in autism, exploring its implications for learning, communication, and daily life.
Understanding Short-Term Memory
Short-term memory is the ability to retain a small amount of information for a brief period. It allows individuals to keep track of information needed for tasks such as following directions, problem-solving, and engaging in conversations. Typically, short-term memory can hold about 7±2 items for around 20-30 seconds without rehearsal.
Short-Term Memory in Individuals with Autism
Research has indicated that individuals with autism may experience unique patterns of short-term memory functioning. Some studies suggest that while they may struggle with certain aspects of short-term memory, particularly verbal working memory, they may excel in visual or spatial memory tasks. This divergence can impact various areas of life, including education, social interactions, and daily activities.
Implications for Learning
In educational settings, short-term memory is vital for comprehension and retention of new information. Children with autism may face challenges in traditional learning environments, especially those that rely heavily on verbal instruction. Teachers can support these students by using visual aids, breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable steps, and allowing extra time for processing information.
For example, instead of providing complex instructions all at once, educators can present information gradually, reinforcing it through repetition and visual supports. This approach can help students with autism better encode and retrieve information, leading to improved academic performance.
Impact on Communication
Communication is another area where short-term memory plays a significant role. Individuals with autism may struggle to keep track of conversations, especially if they are lengthy or filled with complex vocabulary. This can lead to difficulties in understanding social cues, responding appropriately, and maintaining dialogues.
To enhance communication, caregivers and educators can implement strategies that support short-term memory, such as using clear and concise language, providing visual supports, and allowing time for processing responses. These techniques can facilitate better interactions and help individuals with autism express their thoughts and needs more effectively.
Daily Life and Social Interactions
Short-term memory also influences daily functioning and social interactions. Tasks like following routines, remembering appointments, and engaging in social activities can be challenging for individuals with autism if they struggle with memory retention. This can result in increased anxiety and frustration when navigating daily life.
Creating structured routines, using visual schedules, and providing reminders can help support individuals in managing their daily tasks. Additionally, fostering environments that encourage social engagement, such as group activities or structured play, can provide opportunities for individuals to practice social skills while benefiting from short-term memory aids.
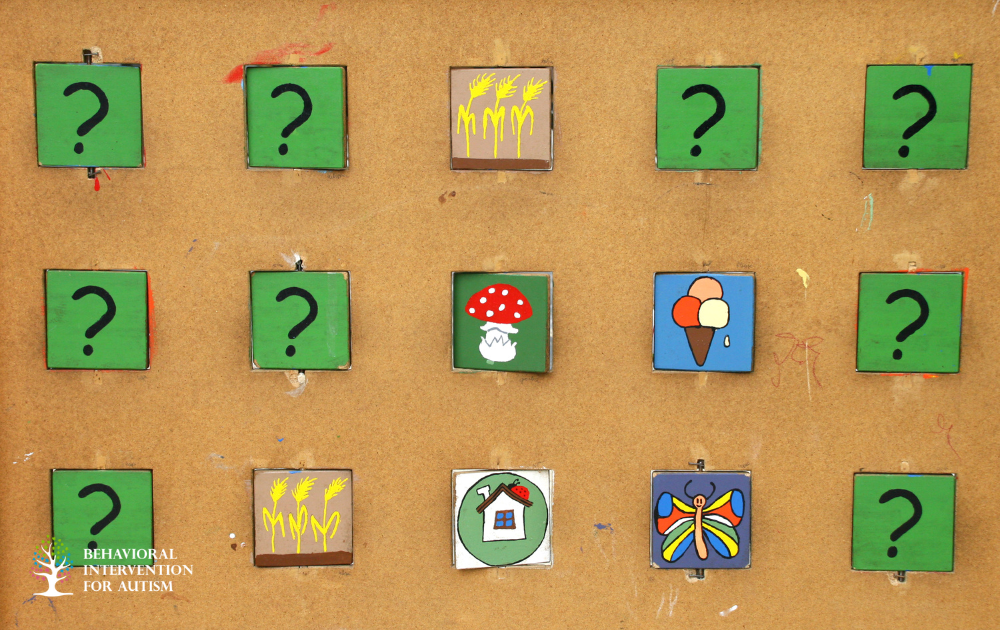

Visual Memory Differences
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often face challenges with visual memory, particularly affecting short-term memory. Two key factors contributing to these difficulties are challenges in identifying inconsistent targets and recognizing error patterns during memory recall.
Difficulty in Identifying Inconsistent Targets
Individuals with ASD often experience more difficulty in identifying an inconsistent target when it is present in a visual scene. This means that when there are objects or elements that do not align or match the overall context, individuals with ASD may struggle to accurately identify and process this discrepancy. This challenge can affect their ability to retain and recall visual information effectively, influencing their overall short-term memory performance.
Error Patterns in Memory Recall
Moreover, studies have shown that individuals with ASD display specific error patterns in memory recall tasks. For instance, in a visual short-term memory task, individuals with ASD were more likely to incorrectly state the presence of a consistent object when it was actually absent from the scene. This discrepancy in memory recall, particularly in relation to consistent and inconsistent targets, highlights the unique ways in which individuals with ASD process and retain visual information.
Understanding these visual memory differences is crucial for caregivers and educators working with individuals with ASD. By recognizing and addressing these specific challenges, tailored interventions and support strategies can be designed to enhance short-term memory skills and improve overall cognitive processing in individuals with ASD. Through targeted interventions and specialized teaching approaches, it is possible to facilitate a more effective learning environment that caters to the unique cognitive needs of individuals with ASD.
Strategies to Support Short-Term Memory
There are several effective strategies that can help individuals with autism enhance their short-term memory skills:
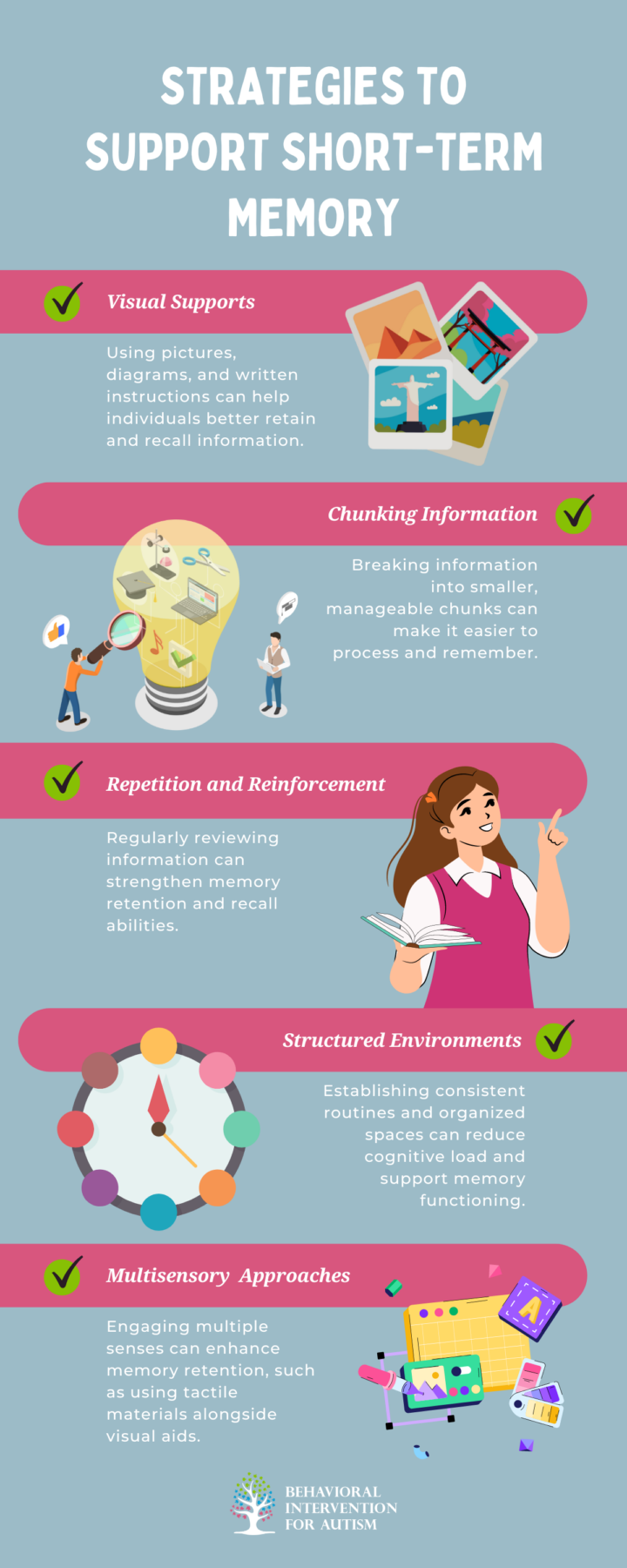
Short-term memory plays a critical role in the lives of individuals with autism, influencing their learning, communication, and daily functioning. By understanding the unique challenges and strengths related to short-term memory in autism, educators, caregivers, and support professionals can implement strategies that foster success and promote independence. With the right support, individuals with autism can thrive and navigate their world more effectively, leveraging their strengths while addressing their challenges.
At Behavioral Intervention for Autism, we offer tailored ABA programs in Florida that focus on enhancing memory skills through engaging and interactive techniques. Our experienced team is dedicated to creating a nurturing environment where individuals can thrive and reach their full potential. If you want to learn more about how our programs can help improve memory and overall functioning, reach out to us today to explore the possibilities!
- 9 Common Obsessions of Children With Autism You Should Know - February 25, 2025
- What is Neurodiversity? A Guide to Embracing Differences - February 25, 2025
- Understanding Hyperfocus in Autism: What It Means and Why It Happens - February 25, 2025
