
Table of Contents
Exploring the intersection of autism and learning reveals a significant impact on the educational experiences of individuals on the autism spectrum. Understanding the challenges that arise is vital for parents and caregivers aiming to support their loved ones effectively.
Overlapping Autism and Learning Disabilities
Research conducted by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reveals a strong correlation between autism and learning disabilities. Approximately 60-70% of individuals with autism also experience a learning disability, highlighting the complex nature of these conditions. This overlap can present unique hurdles in educational settings, requiring tailored strategies and support to address the diverse needs of these individuals.
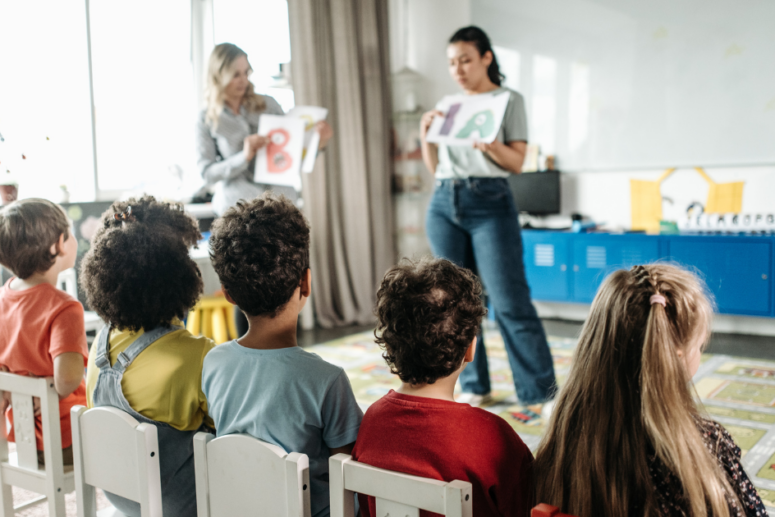
Common Learning Challenges for Autistic Individuals
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can manifest in a variety of ways, impacting cognition, behavior, and communication skills. This, in turn, can lead to common learning challenges for autistic children. These challenges may include difficulties with social interactions, sensory processing issues, executive function deficits, and emotional regulation struggles.
In educational settings, these challenges may manifest as:
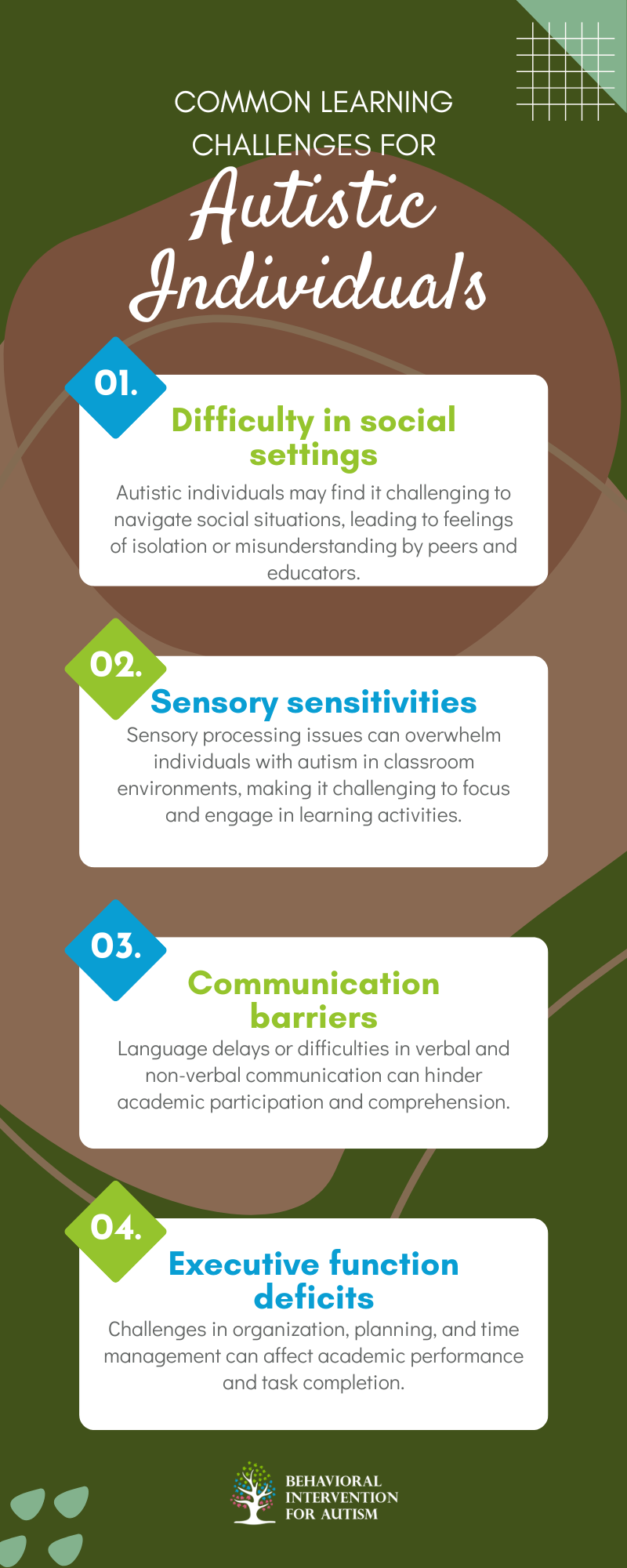
Recognizing and addressing these common learning challenges is crucial in creating inclusive and supportive educational environments for individuals with autism. By understanding the unique needs and differences of autistic learners, parents and caregivers can advocate for appropriate accommodations and interventions to promote academic success and overall well-being.
Impact of Sensory Processing
Understanding the impact of sensory processing in individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is vital to comprehend how autism affects their educational experiences.
Sensory Processing in Autism
Sensory processing plays a significant role in the lives of individuals with ASD, impacting how they perceive and respond to sensory stimuli in their environment. Issues in sensory processing can manifest in hypersensitivity (over-responsivity) or hyposensitivity (under-responsivity) to sensory input, leading to challenges in regulating responses to sensory information.
One common example is hypersensitivity to light or sound, where individuals with ASD may experience discomfort or distress in environments with bright lights or loud noises. On the other hand, some individuals may seek out sensory stimulation, such as repetitive movements or seeking deep pressure to regulate their sensory experiences.
Influence on School Performance
The impact of sensory processing difficulties on school performance in children with autism cannot be understated. Sensory challenges can disrupt a student’s ability to focus, engage in learning tasks, and participate in classroom activities. For example, a child who is hypersensitive to sounds may struggle to concentrate in a noisy classroom environment, affecting their ability to comprehend instructions or engage in group discussions.
Moreover, sensory processing differences can also affect social interactions and emotional regulation in educational settings. Difficulty processing sensory information may lead to sensory overload or meltdowns, hindering the student’s social interactions with peers and educators.
To support individuals with autism in the educational setting, it is crucial for parents and caregivers to work closely with teachers and specialists to create a sensory-friendly environment. Implementing sensory accommodations, such as providing quiet spaces, using visual schedules, or offering sensory tools like fidget toys, can help individuals with autism regulate their sensory experiences and optimize their learning potential.
Recognizing the impact of sensory processing in individuals with autism and implementing tailored strategies to support their sensory needs allows educators and caregivers to create inclusive learning environments that foster academic success and holistic development for those with ASD.

Language Development Delays
Autism spectrum disorder is often associated with delays in language development, which can present significant challenges for individuals on the spectrum. The ability to communicate effectively is crucial for academic success and overall learning experiences.
Challenges in Language Development
Children with Autism typically experience delays in language development, impacting their ability to express themselves verbally and understand language cues. These challenges can manifest as difficulties in speech articulation, vocabulary acquisition, grammar usage, and comprehension of verbal instructions.
Language Development Challenge | Impact on Learning |
Delayed Speech Development | Difficulty expressing thoughts and needs |
Limited Vocabulary | Struggles with understanding and using language |
Grammar Issues | Challenges in forming coherent sentences |
Comprehension Difficulties | Trouble following verbal instructions |
Addressing these language development challenges is essential in creating a supportive learning environment for individuals with autism. Specialized interventions, such as speech therapy and communication strategies, can help improve language skills and enhance overall communication abilities.
Predicting Academic Performance
Language skills play a crucial role in predicting academic performance for individuals with autism. The ability to effectively communicate, comprehend instructions, and engage in classroom discussions directly impacts learning outcomes and educational achievements.
Language Skill | Impact on Academic Performance |
Communication Abilities | Influences participation in classroom activities |
Comprehension Skills | Determines understanding of educational material |
Vocabulary Knowledge | Affects reading and writing proficiency |
Expressive Language | Impacts conveying thoughts and ideas effectively |
Educators and caregivers play a vital role in supporting individuals with autism in developing their language skills to enhance academic performance. Tailored educational plans, assistive technologies, and individualized support services can help mitigate the challenges associated with language development delays and promote success in educational settings.
Understanding the link between language development delays and academic performance is essential for creating inclusive and supportive learning environments that cater to the unique needs of individuals with autism. By addressing these challenges with targeted interventions and adaptive teaching strategies, we can empower individuals on the autism spectrum to reach their full potential in educational pursuits.

Abstract Concept Comprehension
Exploring how autism influences educational experiences reveals that individuals with autism may struggle to comprehend abstract concepts. This difficulty can affect their ability to grasp complex ideas and topics in the classroom.
Difficulties with Abstract Concepts
Autistic children may encounter challenges in understanding abstract concepts. Abstract thinking involves reasoning beyond concrete, observable objects and events, which can be particularly demanding for individuals with autism. This difficulty can hinder their progress in subjects that require conceptual thinking, such as advanced mathematics, science, and literature.
Moreover, abstract concepts are often central to higher-order learning skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. The struggle to comprehend abstract ideas can limit the depth of understanding and the ability to apply knowledge in a practical context, affecting overall academic performance.
Learning Material Challenges
In addition to difficulties with abstract concepts, individuals with autism may face challenges related to learning materials. The presentation and organization of educational content can significantly impact the learning experience for autistic learners.
For instance, complex textbooks, lengthy written assignments, and abstract visual representations may pose obstacles for individuals with autism. The overwhelming amount of information, combined with the abstract nature of the material, can lead to sensory overload and difficulties in processing and retaining information.
To address these challenges, educators and caregivers can utilize tailored learning materials that are more concrete, visual, and interactive. Breaking down abstract concepts into simpler, more digestible units and incorporating hands-on learning activities can enhance comprehension and engagement for individuals with autism.
Understanding the difficulties autistic individuals face with abstract concepts and learning materials is essential for developing effective educational strategies that cater to their unique learning needs and promote academic success. By focusing on individual strengths, providing tailored support, and fostering a conducive learning environment, we can empower individuals with autism to reach their full potential and thrive in educational settings.

Communication and Behavioral Impacts
Considering how autism affects education is essential, as communication and behavioral impacts significantly shape the learning abilities and overall development of individuals with autism.
Effects on Learning Abilities
Autism can have a profound impact on an individual’s learning abilities, affecting various aspects of their educational experience. Autistic individuals may experience challenges in areas such as concentration, information processing, sensory processing, communication, and social deficits. These difficulties or deficits can hinder their ability to effectively engage with learning material, adapt to new concepts, and participate in classroom activities.
One common effect is reduced concentration, which can make it challenging for individuals with autism to stay focused on tasks for extended periods. This can lead to difficulties in retaining information, following instructions, and completing assignments in a timely manner. Information processing difficulties may also arise, making it harder for autistic individuals to absorb new knowledge, organize thoughts, or make connections between different concepts.
Moreover, sensory processing difficulties may further impact learning abilities, as individuals with autism may be hypersensitive or hyposensitive to sensory stimuli. This can lead to distractions, discomfort, or avoidance behaviors in response to certain sensory inputs, affecting their engagement and participation in educational settings.
Implications for Education and Development
The communication and behavioral impacts of autism can have far-reaching implications for education and overall development. These challenges can influence not only academic performance but also social interactions, emotional well-being, and future opportunities for individuals with autism.
In educational settings, the effects of autism on learning abilities may require tailored support and accommodations to help individuals access the curriculum, participate in activities, and reach their full potential. Educators, parents, and caregivers play a crucial role in creating inclusive and supportive environments that address the specific needs of students with autism.
Furthermore, the communication and behavioral impacts of autism extend beyond the classroom and can shape various aspects of an individual’s personal and professional life. Developing effective communication strategies, fostering social skills, and promoting self-regulation are key components in supporting the holistic development of individuals with autism.
Recognizing and addressing the communication and behavioral impacts of autism on learning empowers individuals to navigate the educational landscape with confidence, resilience, and a sense of belonging. Collaborative efforts and a strengths-based approach help create inclusive learning environments that celebrate diversity and promote the holistic well-being of all learners.
At Behavioral Intervention for Autism, we offer comprehensive ABA Therapy in Florida that are tailored to meet the unique needs of each student. Our dedicated team employs evidence-based strategies to enhance learning and promote positive behaviors, ensuring that every child has the opportunity to thrive academically. If you’re interested in discovering how our programs can empower your child’s educational journey, reach out to us today to learn more!
- 9 Common Obsessions of Children With Autism You Should Know - February 25, 2025
- What is Neurodiversity? A Guide to Embracing Differences - February 25, 2025
- Understanding Hyperfocus in Autism: What It Means and Why It Happens - February 25, 2025
