Addressing sensory issues and reducing sensory overload in individuals with autism can be greatly enhanced by using noise-canceling headphones. These headphones utilize active noise cancellation technology to block out external sounds, creating a quieter environment for the listener. Let’s explore the considerations for selecting the right pair.
Considerations for Selection
Choosing the right noise-canceling headphones for an individual with autism requires careful consideration. Every person’s sensory needs and preferences are unique, so finding a pair that suits their specific requirements is essential. Here are some factors to consider when selecting noise-canceling headphones:
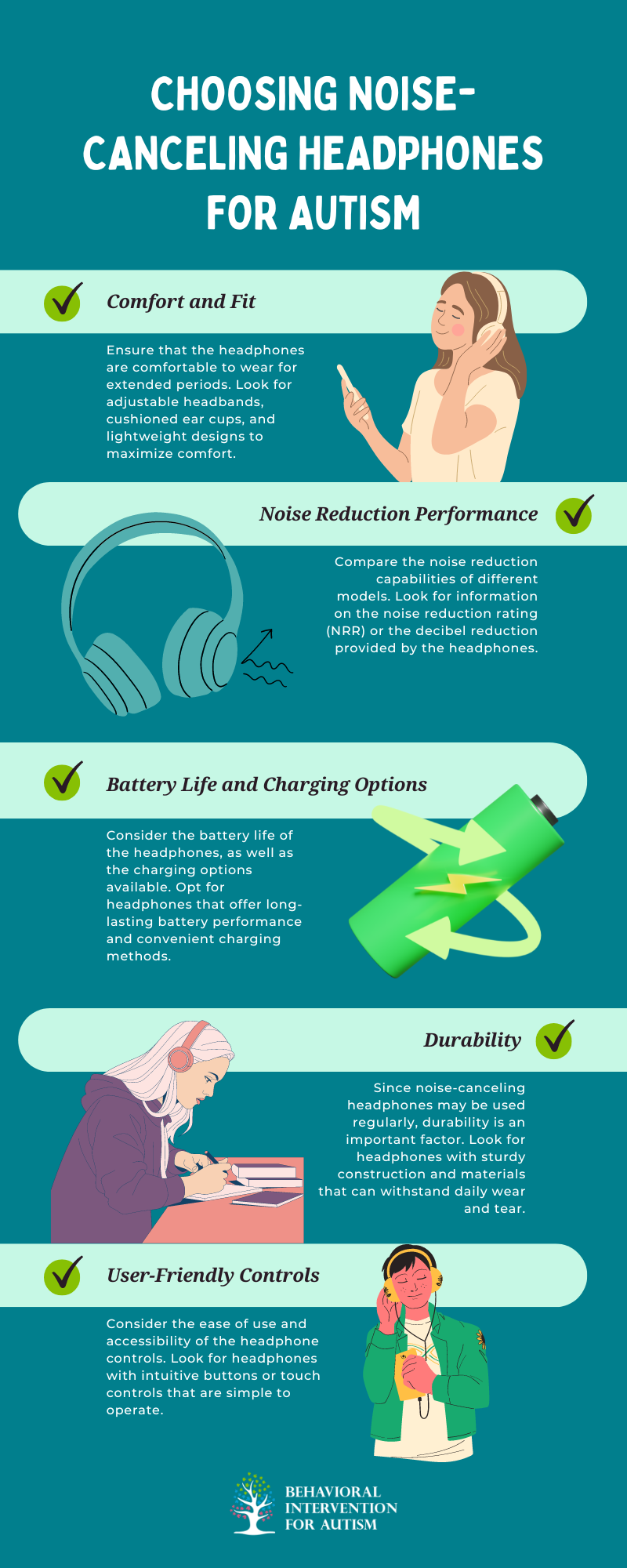
Taking these considerations into account, individuals with autism, along with their parents and caregivers, can choose noise-canceling headphones that cater to their specific sensory needs. This tailored approach promotes a more comfortable and calming auditory environment.
Noise-canceling headphones have proven to be a valuable tool in helping individuals with autism cope with sound sensitivity and sensory overload. By providing a quieter auditory experience, these headphones can make a significant difference in reducing stress, anxiety, and sensory challenges, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals with autism.
Types of Noise Reduction Headphones
To provide relief from sensory overload, two main types of noise reduction headphones are commonly used: active noise canceling (ANC) headphones and passive noise isolation (PNI) headphones.
Active Noise Canceling (ANC) Headphones
Active noise canceling (ANC) headphones are designed to cancel out ambient noise by creating equal but opposite noise. This technology provides a surround sound experience while effectively reducing external sounds. For individuals with autism, these headphones can help in dealing with noise sensitivity, allowing them to reduce stimulation from surrounding sounds.
Research has shown that ANC headphones can have a positive impact on individuals with autism. It is found that autistic children and teens wearing noise-canceling headphones were able to pay attention, focus, stay calm, and participate in loud activities at school without experiencing noise-related anxiety or stress. These headphones provide a way to create a more controlled auditory environment, which can be particularly beneficial in noisy or overwhelming settings.
ANC headphones are often recommended or marketed to help manage noise sensitivities in individuals with autism or ADHD. They are also included as part of sensory toolkits to support autistic children’s access to healthcare.
Passive Noise Isolation (PNI) Headphones
Passive noise isolation (PNI) headphones work by physically blocking out ambient noise. These headphones typically mold to the ear, creating a seal that helps to reduce the amount of external noise that reaches the ear. By blocking out unwanted sounds, PNI headphones allow for lower volume listening, which can be beneficial for individuals with sensory sensitivities.
While ANC headphones actively cancel out noise, PNI headphones provide a more passive approach to noise reduction. They are a popular choice for individuals who prefer a simpler design and do not require electronic components for noise cancellation.
Selecting noise reduction headphones for individuals with autism involves considering factors such as comfort, fit, and personal preference. Some may find active noise-canceling (ANC) headphones more effective, while others might prefer the simplicity of passive noise isolation (PNI) headphones. It’s beneficial to try out different options and assess the individual’s response to determine the most suitable choice.
Understanding the different types of noise reduction headphones can help parents, caregivers, and individuals with autism make informed decisions when seeking relief from sensory overload. By finding the right headphones, individuals can better manage their noise sensitivity and create a more comfortable auditory environment.
Effectiveness and Challenges
The use of sensory headphones for individuals with autism presents both positive outcomes and potential downsides. By understanding these aspects, parents, caregivers, and individuals with autism can make informed decisions regarding the use of these devices.
Positive Outcomes
Sensory headphones, particularly noise-canceling headphones, have been found to provide numerous benefits for individuals with autism. Research and anecdotal evidence suggest the following positive outcomes:
- Noise Reduction: Sensory headphones effectively reduce external noise, which can alleviate sensory overload and prevent sensory meltdowns or shutdowns. These headphones create a quieter environment, allowing individuals with autism to better focus, concentrate, and engage in activities.
- Improved Attention and Focus: Wearing sensory headphones can help individuals with autism maintain attention and focus. By minimizing background noise and distractions, these headphones enable individuals to better concentrate on tasks, whether at home, school, or in public settings.
- Reduced Anxiety and Stress: Sensory headphones can be instrumental in reducing anxiety and stress levels associated with sensory overload. The ability to create a calmer auditory environment can promote relaxation and enhance overall well-being.
- Enhanced Participation: With the help of sensory headphones, individuals with autism may feel more comfortable participating in activities that involve loud noises or crowded environments. This increased participation can lead to greater social engagement and a sense of inclusion.
Parents, caregivers, and teachers have reported positive outcomes when individuals with autism wear sensory headphones, noting improvements in attention, behavior, and overall quality of life.
Potential Downsides
While sensory headphones can provide relief, it’s important to be aware of potential downsides associated with their use:
- Inhibited Communication: Noise-canceling headphones, in particular, may block out important sounds, hindering necessary interactions and communication. Individuals, including children, may not hear important cues, instructions, or warnings while wearing these headphones.
- Overreliance: There is a possibility that individuals with autism may become overly reliant on sensory headphones, using them as a coping mechanism in situations where they may need to develop alternative strategies for managing sensory challenges.
- Social Stigma: Wearing sensory headphones may draw attention or lead to misunderstandings from others who are unfamiliar with their purpose. This social stigma could potentially impact the individual’s self-esteem or social interactions.
It’s important to strike a balance between the benefits and potential challenges of using sensory headphones. Regular monitoring, guidance, and open communication with individuals using these devices can help address any concerns and ensure their proper and effective use.
Understanding the positive outcomes and potential downsides of sensory headphones allows individuals with autism and their support networks to make informed decisions about incorporating these devices into their sensory management strategies. By being well-informed, we can effectively choose the right tools to support sensory needs.
Behavioral Intervention for Autism is committed to helping families navigate these choices through our tailored ABA programs in Florida. Our dedicated team provides high-quality, evidence-based services designed to enhance each individual’s development and well-being. If you’re interested in learning how our programs can make a difference, feel free to contact us today!
























