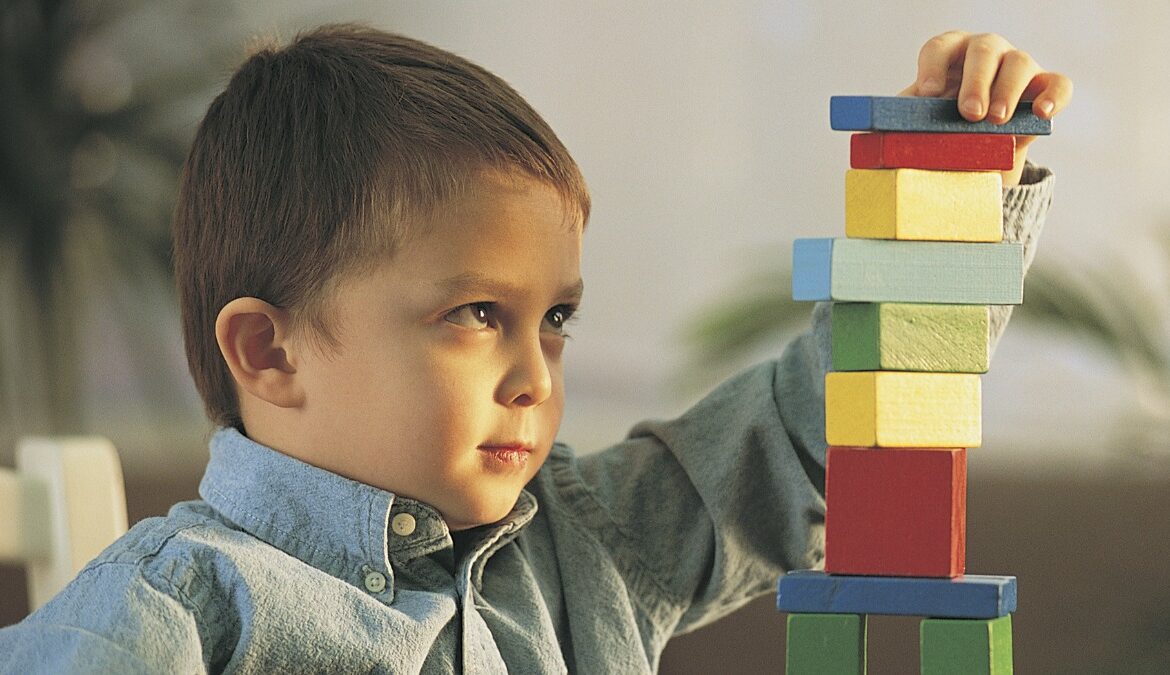
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often develop intense interests or obsessions. These focused interests can bring comfort, joy, and a sense of control, but they can also present challenges for parents and caregivers. Understanding these obsessions can help support children in their development while respecting their passions. Below, we explore nine of the most common obsessions among children with autism.
Trains and Transportation
Many children with autism develop a fascination with trains and other forms of transportation. The predictability, repetitive motion, and structured schedules appeal to their preference for routine and order.
- Obsession with train models and tracks.
- Memorizing train schedules and routes.
- Interest in other vehicles like buses, planes, or subways.
- Enjoying videos or books about transportation.
- Reenacting train journeys at home.
This interest can be used to develop social and learning skills, such as practicing turn-taking when playing with train sets or using transportation themes in educational activities.
Numbers and Patterns
Children with ASD often have a strong affinity for numbers and patterns. The logical and consistent nature of numerical systems provides comfort and predictability.
- Fascination with counting objects repeatedly.
- Memorizing complex mathematical sequences.
- Enjoying puzzles, Sudoku, or pattern games.
- Creating intricate designs with blocks or tiles.
- Developing skills in areas like coding or math.
Encouraging these interests can help strengthen cognitive skills and even open doors to advanced academic opportunities.
Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a common obsession for many children, but this interest is often more intense in kids with autism. The vast history, names, and details offer endless information to absorb.
- Memorizing dinosaur names and facts.
- Collecting dinosaur toys and models.
- Drawing detailed images of various species.
- Watching documentaries and reading books.
- Engaging in role-play as paleontologists.
This passion can support language development, reading skills, and social interaction through shared play and storytelling.
Video Games
Video games provide structured rules and clear objectives, making them appealing to children with ASD. They offer a controlled environment with immediate feedback.
- Spending hours on favorite games.
- Mastering complex game strategies.
- Showing deep interest in game design.
- Discussing game lore and characters in detail.
- Connecting with peers through multiplayer games.
While moderation is key, video games can help with hand-eye coordination, problem-solving, and even social skills through cooperative play.
Animals
Animals often captivate children with autism, offering a non-judgmental presence that can be comforting and engaging.
- Developing strong attachments to specific animals.
- Learning extensive facts about animal species.
- Volunteering at animal shelters or farms.
- Drawing or collecting animal figures.
- Engaging in animal-themed pretend play.
This interest can be nurtured through activities like zoo visits, nature documentaries, or even pet therapy.
Cartoons and Animated Characters
Cartoons and animated characters often attract children with ASD due to their bright visuals, repetitive themes, and predictable storylines.
- Memorizing episodes and dialogue.
- Collecting merchandise like toys and posters.
- Drawing favorite characters.
- Creating stories or acting out scenes.
- Wearing clothing featuring beloved characters.
Using this obsession creatively can encourage storytelling, art, and even social bonding with peers who share similar interests.
Maps and Geography
Children with autism may develop a deep fascination with maps and geography. The structured layout and endless information can be highly engaging.
- Memorizing country names and capitals.
- Drawing detailed maps by hand.
- Studying public transportation systems.
- Using GPS or online maps for fun.
- Learning about cultures and landmarks.
This interest can be used educationally, enhancing knowledge in history, social studies, and even planning real-world trips.
Science and Space
Science and space offer infinite possibilities and logical systems, which can be very appealing to children with ASD.
- Studying planets, stars, and galaxies.
- Conducting simple science experiments.
- Collecting rocks, minerals, or fossils.
- Reading books and watching documentaries.
- Visiting science museums and planetariums.
Supporting this passion can foster critical thinking, curiosity, and academic growth in STEM fields.
Routines and Schedules
Unlike typical interests, some obsessions focus on routines and schedules themselves. The predictability helps children with ASD feel safe and in control.
- Insisting on strict daily routines.
- Creating personal schedules or calendars.
- Following rituals in specific sequences.
- Getting upset when routines change.
- Memorizing others’ schedules.
Maintaining consistent routines while gradually introducing flexibility can help children adapt while feeling secure.
Understanding the obsessions of children with autism allows us to support their growth while celebrating their unique passions. By channeling these interests into educational and social opportunities, we can help them thrive. Each child is different, and their obsessions can be a window into how they see and interact with the world.
Take the Next Step Toward Personalized Support
If your child is navigating intense interests or obsessions, we’re here to help. At Behavioral Intervention for Autism, we specialize in creating individualized ABA therapy programs that focus on your child’s unique needs and strengths. Our dedicated team works closely with families to guide children toward positive growth while addressing common challenges. Ready to make a difference? Connect with us today to explore how our tailored ABA programs in Florida can support your child’s journey. Let’s work together to create meaningful change—reach out now and see the difference compassionate, expert care can make.
Sources: